ERT: 2 minutes read
Image forensics
Image and video forensics are part of the branch of forensics science that deals with multimedia. Its aim is to verify multimedia files data and ascertain whether any manipulation has occurred.
The procedures involved are way harder and longer than they look on most TV crime programmes though! Several steps are required.
First: image and video acquisition.
Most difficulties arise just at the beginning, upon receipt of the data to be analyzed: files are often compressed and/or lo-res, as each device automatically exports them.
If so, information within are scarce or fragmentary and might heavily jeopardize the whole process.
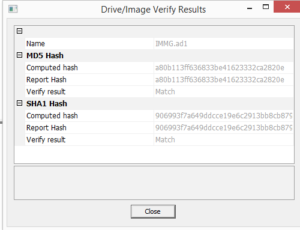
Therefore, whenever feasible, it’s of the utmost importance trying to obtain the original files, either via imaging software, or by following specific export procedures, in order to gather as many data as possible.
Each file has then to be certified by means of double hashing techniques and trusted timestamp, to ensure its validity and integrity, and also its reliability as admissible evidence in a court of law.
Second: file characteristics analysis.
Metadata analysis is a procedure that often provides very useful hints about the nature of given files: it is indeed possible to know when they were first created, last modified and last accessed to; or to identify the type of device and lens used to take the shot; or its shutter speed and aperture.
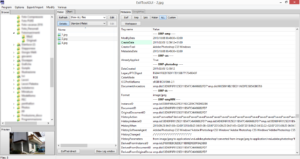
Sometimes metadata can also show the GPS coordinates of where a photo was taken; depending on circumstances, file names can be useful to ascertain their provenance too (e.g. in media sent over What’s App)
The aforementioned markers, together with a sampling from a pool of carefully selected images, may turn out to be of some relevance to the so called “social media forensics” for reconstructing the chain of diffusion of one or more files on social media sites.
Third: image analysis
It is necessary to act on two fronts: a low level one (code analysis) and a specific one (through image manipulation software).
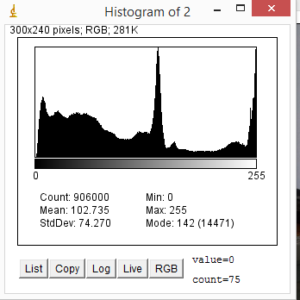
A low level analysis allows to verify the marker integrity of a given file to attest its true extension and recognize traces of any potential steganography (i.e. hidden data), by checking the coherence of its structure.
Image manipulation, instead, applying peculiar filters and effects, allows to enhance the general quality of the image, highlighting details or identifying previous alterations; tools such as level regulations, contrast masks, de-blurring and sharpening filters, error level analysis, resampling and scaling, noise pattern identification, are vital to the process of discovering hidden details or validate the integrity and coherence of the analyzed files.


